
In the Object Oriented approach, it was considered to be an essential step in the specification of business application systems. In that time (the early 1990s) all existing and new modeling techniques to illustrate business processes were consolidated as 'business process modeling languages'.
#Process modeling tools software
In the field of software engineering, the term 'business process modeling' opposed the common software process modeling, aiming to focus more on the state of the practice during software development. New methodologies include business process redesign, business process innovation, business process management, integrated business planning, among others, all "aiming at improving processes across the traditional functions that comprise a company".
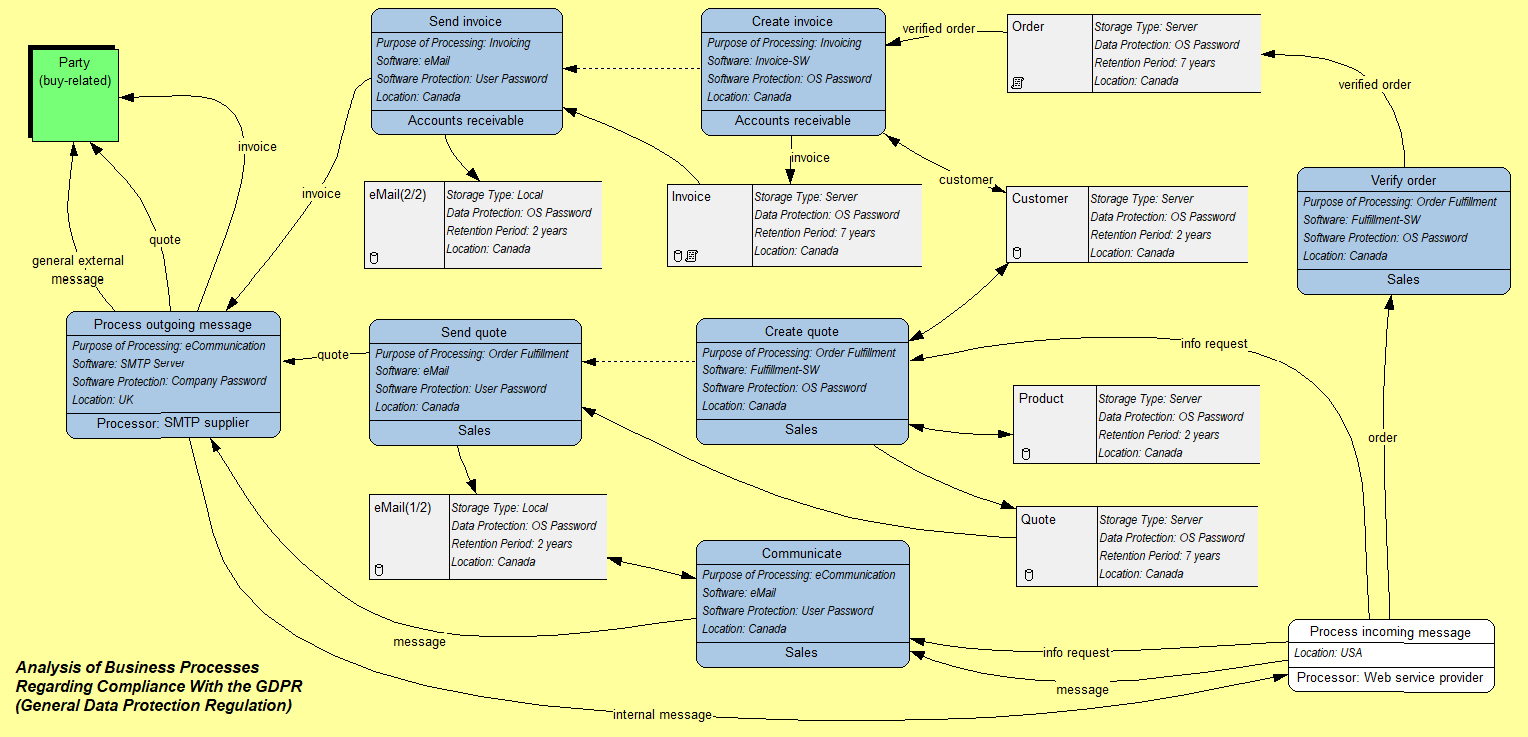
These cross-functional activities have increased significantly in number and importance, due to the growth of complexity and dependence. The traditional modeling tools were developed to illustrate time and cost, while modern tools focus on cross-functional activities. Process thinking looks at the chain of events in the company from purchase to supply, from order retrieval to sales, etc. Companies were encouraged to think in processes instead of functions and procedures. In the 1990s the term ' process' became a new productivity paradigm. It was not until the 1990s that the term became popular. His idea was that techniques for obtaining a better understanding of physical control systems could be used in a similar way for business processes. Williams in his 1967 article 'Business Process Modelling Improves Administrative Control'. The term 'business process modeling' was coined in the 1960s in the field of systems engineering by S. Still, these represent just a fraction of the methodologies used over the years to document business processes. Among the modern methods are Unified Modeling Language and Business Process Model and Notation.

The Gantt charts were among the first to arrive around 1899, the flow charts in the 1920s, Functional Flow Block Diagram and PERT in the 1950s, Data Flow Diagrams and IDEF in the 1970s. Techniques to model business process such as the flow chart, functional flow block diagram, control flow diagram, Gantt chart, PERT diagram, and IDEF have emerged since the beginning of the 20th century. With advances in software design, the vision of BPM models becoming fully executable (and capable of simulations and round-trip engineering) is coming closer to reality. In practice, a management decision to invest in business process modeling is often motivated by the need to document requirements for an information technology project.Ĭhange management programs are typically involved to put any improved business processes into practice. The business objective is often to increase process speed or reduce cycle time to increase quality or to reduce costs, such as labor, materials, scrap, or capital costs.
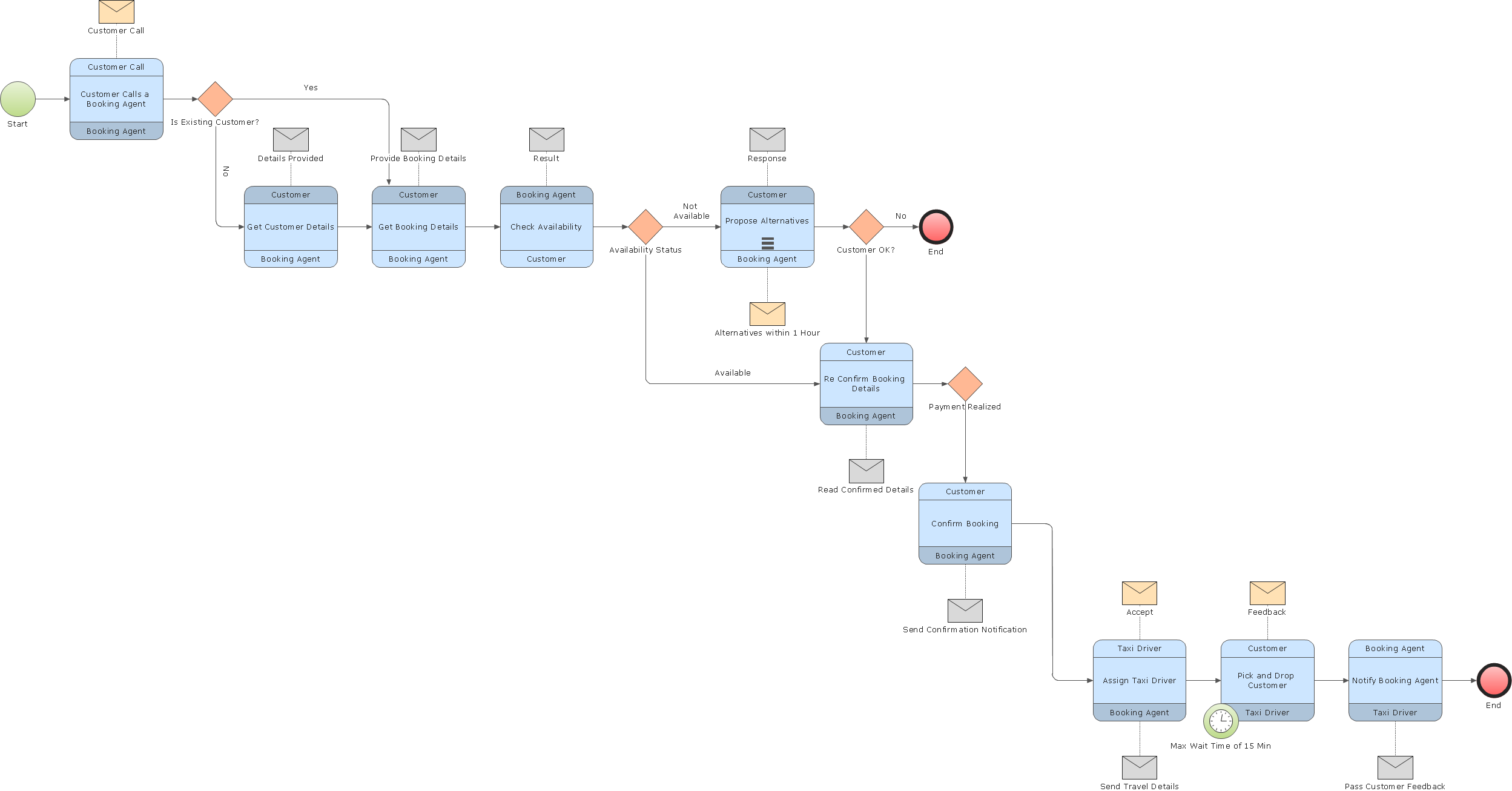
Alternatively, the process model can be derived directly from events' logs using process mining tools. BPM is typically performed by business analysts, who provide expertise in the modeling discipline by subject matter experts, who have specialized knowledge of the processes being modeled or more commonly by a team comprising both. Example of business process modeling of a process with a normal flow with the Business Process Model and Notationīusiness process modeling ( BPM) in business process management and systems engineering is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current business processes may be analyzed, improved, and automated.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
